Abusing windows accessibility features | sethc.exe | sticky keys | persistence and privilege escalation
https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1546/008/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dIuQ2sUsZEo
sethc.exe resides on windows\system32 folder. in sethc.exe even administrators does not have full access. only the owner of the system which you can say trustedinstaller has the full access. but you can change the trustedinstaller by clicking the Advanced options. you can change the trustedinstaller by clicking the change button and add a local user who has admin rights.
here action is performed in a domain environment. but you can add your local user as well. as an example i had added my username which is Avi who has admin rights on the system.
now sethc owner has been changed. as you are owner now of sethc so you can now decide whom you want to give full access.
now click on edit. now you can change permissions. give administrators full control permissions. click yes on the popup.
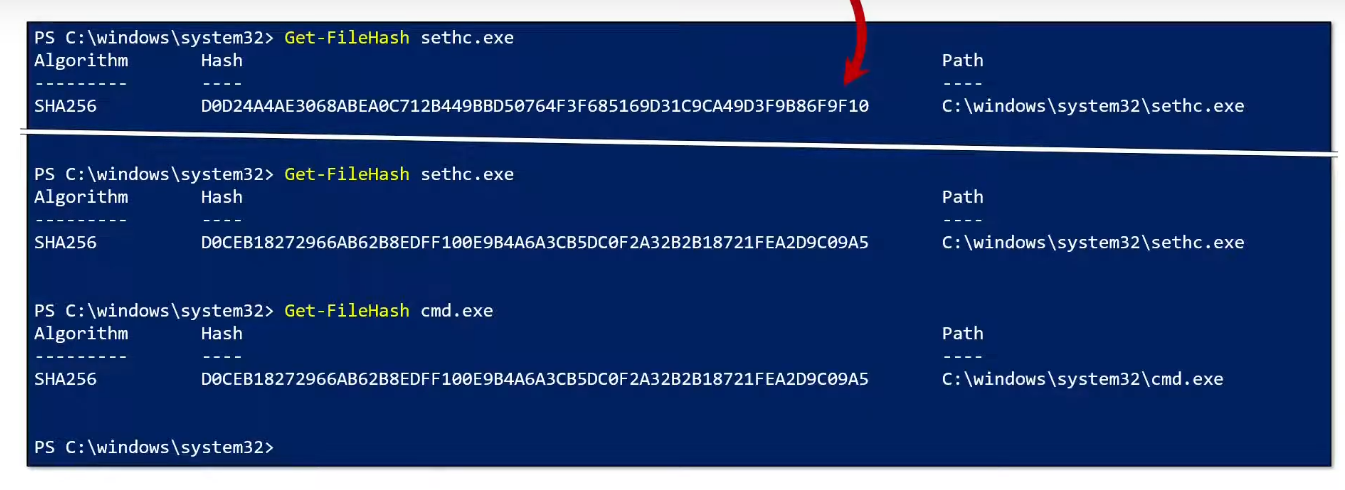
now you can rename the file. so rename the sethc.exe to sethc.exe.bak
then make a copy of cmd.exe. then you shall get cmd - Copy.exe
now rename cmd - Copy.exe to sethc.exe
done.
now whenever you press 5 times shift key, a command prompt will open. and will be running of the current user session. if you are login as admin then the command prompt will also launch in the context of that admin rights. during the system is locked then it will run in the context of nt authority\system
it will give you persistency, elevation of privilege because it will still work if the system rebooted, or admin user get disabled or password changed scenario. it is still work if the system is accessed by remotely.
Detection:
as this is not a malware activity but good AV like windows defender can also detect this behavior change anomaly. however as you are running this as local admin so from the Action setting on defender, you can allow on this device.
but there is a way where you can specify that threats cannot be allowed on this device. here is how you can tightend up in an enterprise environment.
expand the windows components.
disabling local list merging. it forces microsoft defender to ignore any configuration changes or exception which have been defined on the local machine by any user. instead it says use the values set on the group policy. once the group policy is updated (gpupdate /force) the exception we added earliar will be deleted from the allowed threats and you cannot make the exception again.
note:
replacing accessibility feature binaries needs to be digitally signed for x64 systems. the binaries must reside in Windows\System32 folder. and it must be protected by windows file or resource protection (WFP/WRP).






Comments
Post a Comment